Francisco de Goya, a deaf artist, is frequently regarded as the father of modern art, a visionary who utilized his artistic talents as both a tool for commentary and a reflection of societal conditions. In a period characterized by turmoil and transformation, including the Peninsular War, his works expose the profound complexities of human experience and the prevailing political strife. Goya's trajectory, from modest beginnings to his ascension as the official painter to the Spanish court, comprises a rich narrative of personal achievements intertwined with significant challenges. An exploration into what motivated him, including the influence of Enlightenment ideals, to produce such impactful imagery raises questions about how his life experiences informed his lasting legacy. The examination of Goya reveals not only the man behind the masterpieces but also the controversies surrounding his work that continue to provoke discussion in contemporary discourse.
Who Was Francisco De Goya?

Francisco Goya, a distinguished Spanish artist born on March 30, 1746, in Fuendetodos, Spain, is widely recognized for his significant contributions to the art world during a tumultuous historical context characterized by the Peninsular War and political corruption, and passed away on April 16, 1828.
Goya's artistic evolution is exemplified by his transition from a court painter under Charles IV to a leading figure representing Enlightenment ideals. His notable works, including 'The Disasters of War', 'The Naked Maja', 'The Clothed Maja', and 'The Third of May', are imbued with profound emotional and political significance, reflecting his artistic maturity and distinctive vision.
Early Life and Education
Francisco Goya's early life in Fuendetodos, Spain, significantly contributed to his subsequent achievements as a prominent Spanish artist, marked by a profound passion for art from a young age, including his time as a gilder.
Raised in a small village, he was immersed in the rich cultural heritage of Spain, which ultimately led him to pursue formal education in art at the Royal Academy of San Fernando.
There, he had the opportunity to learn from distinguished artists such as Anton Raphael Mengs and José Luzán, while also drawing inspiration from the masterpieces of Diego Velázquez and Rembrandt, influencing his Black Paintings.
What Was Goya's Childhood Like?
Francisco Goya's childhood in the picturesque village of Fuendetodos, Spain, was characterized by a close-knit family and an early exposure to artistic influences that would ultimately shape his future career as a prominent Spanish artist.
Nestled amidst the rolling landscapes of Aragón, this quaint village provided a vibrant backdrop for Goya’s formative years. During his upbringing, he was profoundly influenced by the artistic heritage of his family, particularly by his father, who was an avid painter. This familial support played a pivotal role in encouraging his creative pursuits and fostering the confidence necessary to explore his artistic talent.
The local traditions, including festivals that celebrated folklore and religious customs, introduced the young artist to a rich palette of colors, emotions, and themes that would later become prominent in his oeuvre. Goya's experiences in Fuendetodos, immersed in the expressive culture and the way of life of the community, were instrumental in nurturing his unique perspective.
Additionally, the local artisans, with their diverse crafts, inspired him to adopt a variety of techniques, thereby laying the groundwork for his eventual mastery of painting and printmaking, including La Tauromaquia and Los Disparates.
Where Did Goya Study Art?
Goya pursued his formal art education at the esteemed Royal Academy of San Fernando in Madrid, where he refined his skills under the tutelage of distinguished artists such as Anton Raphael Mengs and José Luzán.
His time at this prestigious institution extended beyond the mere mastery of techniques; it encompassed a comprehensive curriculum that emphasized the significance of classical art principles alongside innovative methodologies. The academy fostered a profound appreciation for both traditional and contemporary styles, creating an environment conducive to the growth of aspiring artists.
Through his engagement with his mentors, Goya cultivated a unique synthesis of realism and expressionism that would come to characterize his later works. Notably, the insightful critiques provided by Mengs and Luzán significantly influenced Goya's understanding of light, shadow, and emotion, thereby impacting his approach to both painting and printmaking.
This mentor-student relationship was pivotal in Goya's artistic development, and the invaluable lessons acquired at the academy resonated throughout his career. Ultimately, these formative experiences at the Royal Academy fortified Goya’s determination to challenge artistic conventions, culminating in the creation of iconic pieces that embodied his audacious vision.
Career and Achievements

Francisco Goya's distinguished career as a Spanish artist is marked by a significant evolution, commencing with his appointment as court painter to Charles IV. During this period, he produced several notable works that exemplify both his artistic maturity and his keen social commentary.
Goya's masterpieces, such as 'The Disasters of War', 'The Naked Maja', 'The Clothed Maja', and 'The Third of May', not only demonstrate his technical expertise but also articulate profound insights into the human condition, politics, and the challenges of his era.
This body of work has firmly established Goya as a pivotal figure in the art world and a court painter to Charles IV.
What Were Goya's Early Artworks?
Goya's early artworks, particularly his series *Los caprichos*, exemplify his innovative artistic style and provide a significant social commentary that captures the essence of Spanish society in the late 18th century, reflecting his artistic maturity.
These works simultaneously reveal the complexities of human nature and the societal issues prevalent during his time.
Created between 1797 and 1798, these etchings serve as a profound critique of the moral and cultural landscape of Spain, addressing themes such as superstition, corruption, and the folly of the upper classes. In *Los caprichos*, Goya employs a variety of techniques, including the use of light and shadow and intricate line work, to produce striking imagery that resonates with viewers on multiple levels.
- His utilization of satire facilitates a deeper understanding of societal flaws.
- The dark and whimsical nature of the illustrations highlights his unique perspective on reality.
By integrating fantastical elements with social realism, Goya invites the audience to engage in a critical reflection on their own beliefs and the world surrounding them. This body of work not only established Goya as a pioneering figure in the art world but also laid the foundation for future movements that explored similar themes of humanity and societal critique.
How Did Goya Become Court Painter to the Spanish Crown?
Goya's rise to the prestigious position of court painter to the Spanish Crown was characterized by his exceptional talent, which captured the attention of Charles IV. This recognition led to significant accolades that solidified his reputation within the art world.
This pivotal moment in his career not only attested to his artistic abilities but also resulted from several key milestones that preceded it. Early in his journey, Goya refined his skills at the Royal Academy of Fine Arts of San Fernando, where he absorbed classical techniques and the rich traditions of Spanish painting. His exposure to esteemed artists, coupled with a deep understanding of light and composition, greatly influenced his subsequent work.
The appointment as court painter fundamentally altered his artistic trajectory, providing him with access to royal patronage that facilitated greater experimentation and exploration of themes such as identity and society. This role ultimately established him as a significant figure in the transition from the Rococo style to a more modern approach in art.
What Are Some of Goya's Most Famous Works?
Among Francisco Goya's most renowned works are *The Disasters of War*, *The Naked Maja*, *The Clothed Maja*, and *The Third of May*, each serving as a testament to his artistic maturity and profound engagement with the socio-political landscape of his era.
These iconic pieces not only showcase Goya's technical expertise but also demonstrate his remarkable ability to capture the human condition amidst chaos, conflict, and societal transformations. Goya's legacy is intricately intertwined with themes of conflict, identity, and morality, resonating deeply with subsequent generations of artists and intellectuals.
For instance, in *The Disasters of War*, the harrowing imagery functions as an unflinching critique of violence, while *The Third of May* starkly illustrates the tragedy of loss and the struggle against oppression.
- The stark contrasts utilized in *The Naked Maja* and *The Clothed Maja* by the Spanish artist Francisco Goya challenge traditional representations of femininity and provoke critical reflection on the societal norms of the time.
- These works not only exhibit Goya's distinctive techniques but also invite viewers to confront the complex realities of 18th-century Spain, particularly during the Peninsular War.
Ultimately, Goya's contributions continue to influence contemporary discourse, rendering his reflections both timely and timeless, especially through works like The Third of May.
Personal Life and Legacy in Fuendetodos, Spain

Francisco Goya's personal life, characterized by familial connections and a complex relationship with the Spanish Royal Family, significantly influenced his legacy as a prominent figure in the art world, especially during his time as a painter at the Royal Tapestry Factory.
Goya's experiences, including his battles with illness, not only shaped his artistic expression but also contributed to the enduring impact of his works, as seen in the Black Paintings. This culmination of factors established him as a pivotal figure in the evolution of modern art.
Did Goya Have a Family?
Francisco Goya's family life included a marriage to Joséfa Bayeu, with whom he had several children, providing a significant personal context for his artistic endeavors. This marriage not only served as an emotional foundation for Goya but also had a substantial impact on his creative expression, inspiring series like Los caprichos.
The influence of family dynamics is evident throughout his body of work, as domestic life frequently permeated his paintings and drawings, transforming ordinary moments into extraordinary reflections of the human experience, an approach mirrored by artists like Rembrandt.
Goya and Joséfa had multiple children, and their presence undoubtedly inspired the themes of innocence and familial connection that are prevalent in many of his works.
- Children were often depicted in tender moments, illustrating the warmth of parental bonds.
- His son, for example, may have prompted particular explorations into youth and the passage of time, similar to themes in La Tauromaquia.
Through these personal experiences, Goya effectively conveyed a depth of emotion and authenticity that resonated with audiences, allowing his art to transcend mere visual representation and evolve into a profound commentary on life itself.
What Was Goya's Relationship with the Spanish Royal Family?
Goya's relationship with the Spanish Royal Family, particularly in his capacity as court painter to Charles IV, was marked by both admiration and the intricate political dynamics that influenced his artistic endeavors. This complex association not only afforded the artist substantial patronage but also positioned him at the heart of the shifting allegiances and political tensions characteristic of late 18th and early 19th century Spain. As historical events progressed, Goya's critiques of the monarchy began to surface, subtly interwoven into his masterpieces.
His paintings and engravings often mirrored the socio-political turbulence of the era, showcasing not only the grandeur of royal life but also the underlying currents of discontent. These interactions inevitably shaped his artistic vision and elevated his social standing, establishing him as a pivotal figure within the court while simultaneously positioning him as a discerning observer of its eventual decline.
- Influence of the Peninsular War on Goya's thematic explorations, evident in The Disasters of War.
- Transition from royal patronage to the expression of social criticism.
- His works served as a conduit between art and societal transformation.
Through this lens of profound complexity, Goya's legacy intertwines with that of the Royal Family, providing valuable insights into the delicate balance of power, artistry, and the human experience during a transformative period in Spanish history.
How Did Goya's Illness Affect His Art?
Goya's struggles with illness, including his eventual deafness, significantly influenced his artistic expression, resulting in new themes and styles that defined his later works.
The impact of serious health challenges on an artist's creativity is often substantial, and in Goya's case, it transformed his approach to his craft. This transformation is particularly exemplified in works such as "Saturn Devouring His Son," where the themes of isolation and despair resonate profoundly. The distorted figures and haunting imagery evoke a sense of anguish that reflects the artist's own fears and vulnerabilities.
In a similar vein, in "The Black Paintings," Goya delves into psychological torment and mental instability, adopting a darker palette and more abstract themes, a departure from Enlightenment ideals. His later lithographs, especially those in the series "The Disasters of War," present a raw and unfiltered commentary on human suffering, revealing his acute awareness of the turmoil surrounding him during the Napoleonic Wars.
Through these examples, it is evident that Goya's health issues served as a catalyst for a profound transformation in his artistic vision, as he grappled with the shadows of his experiences.
What Is Goya's Legacy in the Art World?

Francisco Goya's legacy in the art world is monumental; he is often regarded as a precursor to modern art, having influenced countless artists and movements with his innovative techniques and profound themes.
His exploration of the darker aspects of human nature, along with the socio-political climate of his time, resonates powerfully even today. Goya's social critique and emotional depth serve as a foundation for subsequent movements, including Expressionism and Surrealism. Prominent artists such as Edvard Munch and Pablo Picasso found inspiration in Goya's capacity to capture the human condition and convey visceral emotion through his art.
- Goya's work frequently addressed themes of violence, oppression, and psychological turmoil, encouraging other artists to engage with similar subjects.
- This emphasis on social justice remains particularly relevant in contemporary contexts, where artists continue to challenge societal norms and raise awareness of injustices through their creative expressions.
His influence is evident in modern multimedia art forms, where the integration of traditional techniques with contemporary issues reflects Goya's enduring impact on the artistic landscape.
Controversies and Criticisms
Throughout his career, Francisco Goya encountered numerous controversies and criticisms, particularly due to his audacious representations of political corruption and societal injustices that challenged the prevailing norms of his era.
What Are Some Controversial Aspects of Goya's Work?
Goya's works, particularly *The Disasters of War* and his later *Black Paintings*, are frequently regarded as controversial due to their stark portrayals of violence and despair, which reflect the tumultuous political landscape of his time.
These pieces provide a profound examination of human suffering and the ethical implications of conflict, eliciting powerful reactions from both the public and critics. Many viewers are confronted with uncomfortable truths regarding the nature of humanity and the consequences of war.
- The graphic depictions in *The Disasters of War* emphasize the brutal realities faced by both soldiers and civilians, provoking intense debates surrounding morality in art.
- Conversely, the haunting imagery of the *Black Paintings* serves as a compelling commentary on the darkness that can permeate the human psyche.
In this manner, Goya's work challenges established norms and fosters dialogue, prompting reflection on themes that remain relevant in contemporary society.
What Criticisms Did Goya Face During His Lifetime at the Royal Academy of San Fernando?
Throughout his lifetime, Francisco Goya encountered criticisms from both conservative and progressive factions regarding his political commentary and the emotional intensity of his artwork, which frequently elicited strong reactions.
These controversies underscore how Goya's work served as a reflection of the societal tensions of his time. On one hand, conservative critics denounced his audacity to challenge established norms and authority through provocative imagery and themes. They perceived his portrayals of war, suffering, and human folly as an affront to traditional values, questioning the appropriateness of such raw emotional expression within the realm of art.
Conversely, progressive audiences lauded his willingness to confront the harsh realities of existence, appreciating his capacity to articulate the struggles of the common people against oppressive regimes. This dichotomy fostered robust discussions regarding the role of the artist in society and the responsibilities that accompany such a potent voice.
Through this ongoing dialogue, Goya's legacy has continued to evolve, as subsequent generations of artists draw inspiration from his audacious spirit and unparalleled ability to encapsulate the zeitgeist of his era.
The video highlights some of the most notable works of Francisco Goya, including 'The Disasters of War' and his famous 'Black Paintings'.
Frequently Asked Questions
Who is Francisco De Goya?
Francisco De Goya (1746-1828) was a renowned Spanish painter and printmaker, considered one of the most important Spanish artists of the late 18th and early 19th centuries, born in Fuendetodos, Spain.
What is Francisco De Goya known for?
Goya is best known for his paintings, especially his portraits and depictions of Spanish royalty and the social and political turmoil of his time. He also created a series of prints titled "Los Caprichos" that criticized the social and political issues of his era. Among his notable works are 'The Naked Maja' and 'The Clothed Maja'.
Why is Francisco De Goya significant in the art world?
Goya's works are considered a bridge between the old masters and modern art, making him a key figure in the development of Western art. He is also credited with being one of the first artists to capture the darker aspects of human nature in his works, influenced by artists like Diego Velázquez and Rembrandt.
When did Francisco De Goya live?
Goya was born in 1746 and lived until 1828. He was born and spent most of his life in Spain, with a brief period in France during the political upheaval in his home country. He passed away in Bordeaux, France.
What style of art did Francisco De Goya use?
Goya's early works were influenced by the Rococo style, but he later moved towards a more realistic and raw style. He is often associated with the Romantic movement due to the dark and emotional themes present in his works. Goya's art reflects Enlightenment ideals and the impact of the Peninsular War.
What are some of Francisco De Goya's most famous works?
Goya's most famous works include "The Third of May 1808", "Saturn Devouring His Son", and "The Nude Maja". He also created many portraits of Spanish royalty, including King Charles IV and Queen Maria Luisa. Goya also produced the series 'La Tauromaquia' and 'Los Disparates'.

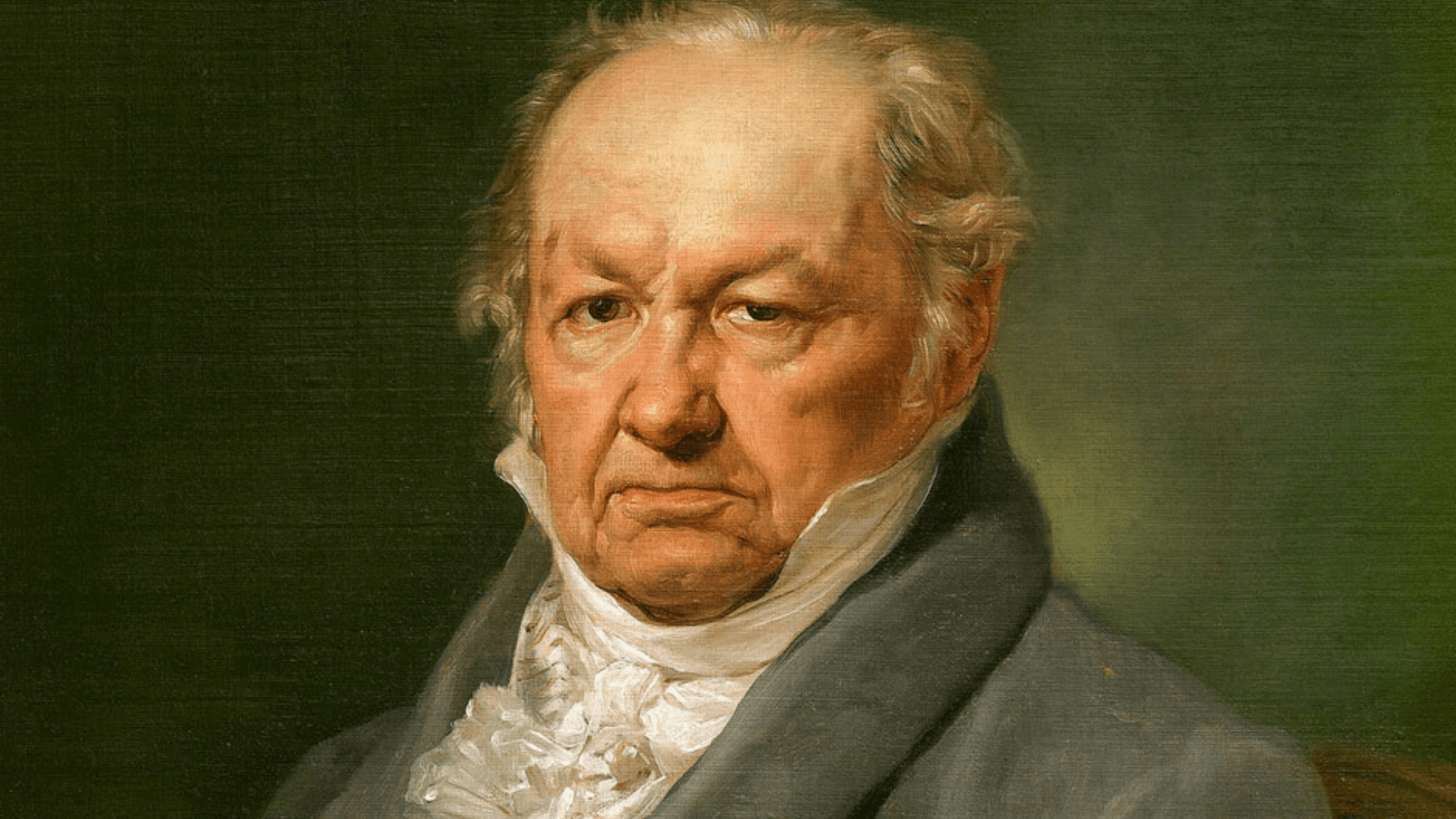
Who Is Rembrandt ?
Andy Warhol vs Modern Pop Art: What's Your Style?